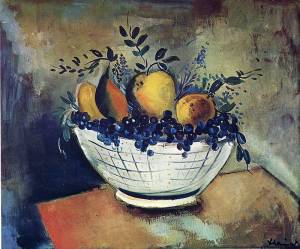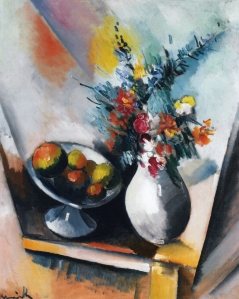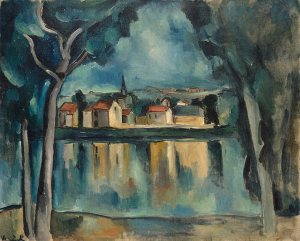Receive e diary posts.
~ Maurice de Vlaminck ~ …
Maurice de Vlaminck French painter and graphic artist, who is considered the ancestor of expressionism among the Fauves. In his landscapes, still lifes and portraits, he lifted up to the level of self-color painting.
French painter Vlaminck was born into a musical family, his father was Fleming, and his mother – from Lorraine, in 1878 his family moved to Le Vesinet. At 16, the young man left home and worked as a driver, cyclist and mechanic. After he had been ill with typhoid fever, he had to leave the career – he played the violin in the orchestra and gave music lessons. In 1894, Vlaminck married Suzanne Burley (in 1905 the divorce, a second marriage with Burt Combe).
As a result of a railway accident Vlaminck he became acquainted with the artist Andre Derain, which then rented a studio on the island of Chatou-on-Seine. The following year, Derain introduced Vlaminck, Henri Matisse. Thus was formed the core areas, which later give the name of “Fauvism”. Self-taught, he was proud that he had never attended any of the Academy or in the studio, not even in a museum. Art classes nevertheless did not give him the opportunity to feed themselves, and he had to work a musician in a variety show in Montmartre and billiards. In addition, he wrote erotic stories that illustrated Derain.
In 1904, in the gallery of Berthe Weill, one of his paintings was first shown to the public. In 1905, the artist participated in the “Salon d’Automne” and the Salon des Independants in the hall of “wild” with Derain, Matisse, Marquet, Jacks, Friese, Mangenom, Puy, Braque, Van Dongen and Kamuanom. The works consisted of clean, unbreakable color planes. Like Matisse, Derain and Raoul Dufy, he refused to subtle shades and color transitions that prevailed among the Impressionists. The space in which artists present their work, the critic Louis voxel compared with cage for wild animals – ?cage aux fauves?. After that, representatives of the movement in painting (the French version of expressionism) were named as “Fauves”.
Like other Fauves, Vlaminck in his landscapes and still lifes form of subordinated color. An example occurred in 1906 “Landscape with red trees.” He wrote almost without contours and refused from the traditional perspective of constructing a picture.
In 1906, Vollard bought his paintings, and the artist is gradually beginning to emerge from poverty and to earn his painting. Vlaminck’s first solo exhibition was held at Vollard’s gallery in 1907. During World War Vlaminck worked as a draftsman at a defense plant. After the war he returned to his expressionist painting. Due to the dramatic effects of light and shade, and cool colors Vlaminck paintings evoke the ominous mood of the viewer. In 1919 he bought a house in the countryside near Paris Valmondua that in 1925 traded at a small land holdings la Ruelle Gadilere. There is secluded from the urban bustle artist devoted himself to work on zemle.On was the author of twenty novels, poems and essays (“All this”, 1903: “Soul dummies”, 1907, “dangerous turn” 1929 “Portrait of before death” 1943: “Landscape and figure”. 1953).
Art Vlaminck, restless and instinctive, noted the immediate and passionate love for nature. Bright individuality master showed already in his first paintings (1899-1903). So, a few caricature portrait “Papa Buzhyu” (about 1900, Paris, National Museum of Modern Art, Centre Pompidou) executed in broad strokes, as will soon be working Soutine: it’s a real ballet paint.
In 1901 Vlaminck starts using pure color, which he opened the exhibition Van Gogh Gallery. Bernheim-Jeune. Influence of Dutch painter manifested later in such films as “Interior” (1903-1904) and “The Reaping in the storm” (1906), which resemble the later landscapes Van Gogh painted in Auvers-sur-Oise. Vlaminck soon became one of the leaders of Fauvism (1904-1907). It completely breaks with the style of the preceding period, and enthusiastically opens principles of Fauvism. He almost did not mix the colors: red, green, blue, yellow colors are often used in pure form (“Landscape with red trees. Street in Marly” 1905, “Marly-le-Roi,” in 1906, Paris, Musée d’Orsay) .
In his works, the artist often combines separate brushstrokes and uniform geometric vangogovskie strokes in the form of commas. “Chatou” (1907, Paris, Musee National Art Moderne, Centre Pompidou) – one of the first paintings by Vlaminck, which manifests the influence of Cezanne, which will be felt in his works up to 1910, and sometimes later (“House with a shed”, 1920 Paris, the City Museum of Contemporary Art).
In 1910 the artist’s admiration for Cézanne leads to cubism. But soon enough, however, Vlaminck felt that his freedom as an artist was constrained rational artistic conception of Cubism. Disclaimer Vlaminck sum their works under the theoretical basis led him to break with the intellectual Derain.
In 1936, the Carnegie Institute in New York has carried out successful presentation of works Vlaminck in the United States. After the entry of the German troops in France (1940), the artist went to Normandy, but pretty soon returned to his rural home. During the occupation, Vlaminck, as a member of the League of anti-fascists, joined (in 1941) to a group of French artists, which the Germans sent on a trip to Germany for propaganda purposes. Two years later, in his book, “Portrait of before his death,” he attacked with violent attacks on contemporary art at the time and got a lot from the Nazis. After the war, Vlaminck was brought before a special court on charges of collaboration, which, however, was removed from it.
In the postwar years Vlaminck wrote paintings predominantly mentalizing again approached in the early 50s to their early Fauvist works, it remains true to this style until his death (dark shades and lead tones). It uses vermilion, black and white colors, which gives it a romantic landscape under stormy bong or not during a storm dramatic and violent character. A favorite subject of the artist becomes expensive and wheat fields. The artist has created numerous watercolors, woodcuts and lithographs, which are subject to the same as that of his paintings, a style. However, their history is rather difficult to determine because they tend not dated.
In 1954, he represented his country at the Venice Biennale, regaining its former respect, which to some extent has been lost because of accusations of collaboration. The first major retrospective of the work Vlaminck took place in 1956 – though not in the public and private art “Gallery Sharpenter” in Paris. Two years later, the artist died in Ruelle la Gadilere the age of 82.